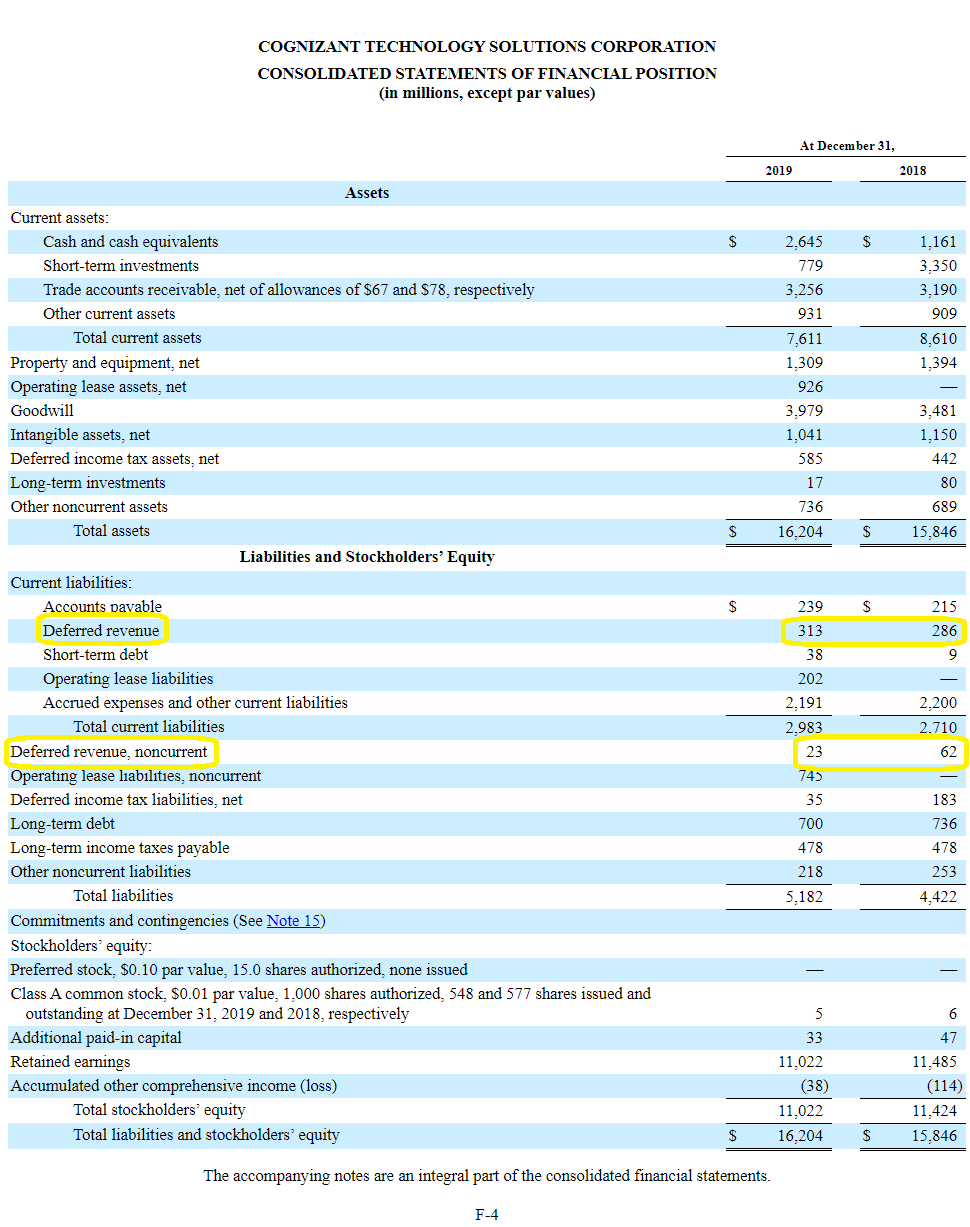
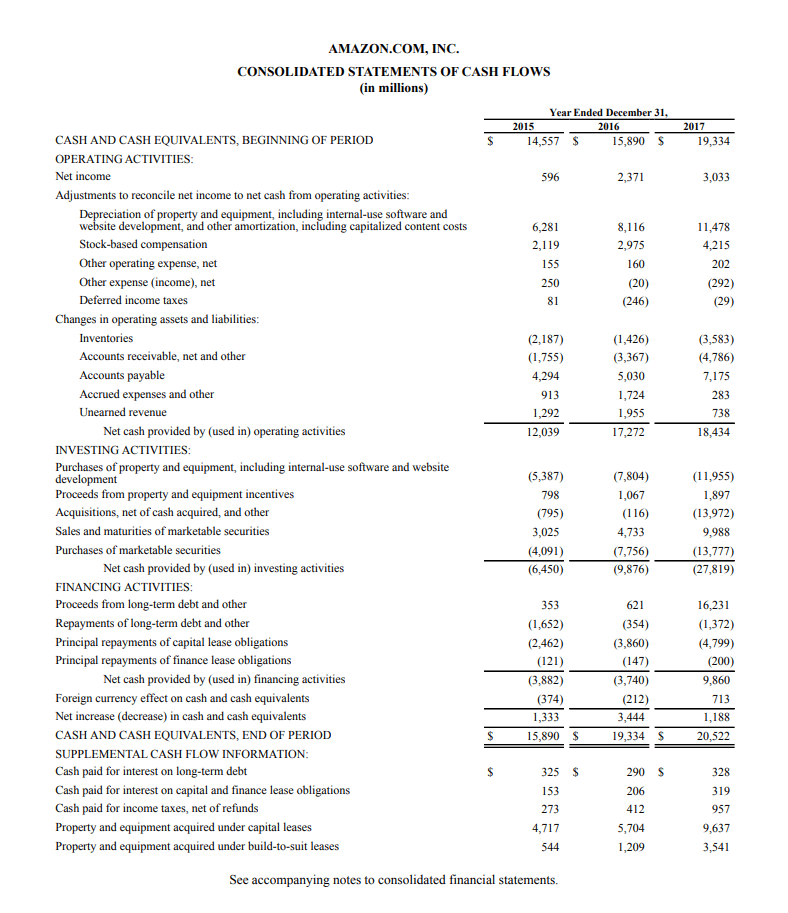
Exemplary Treatment Of Tax In Financial Statements

Presentation choices and impact on financial statements In respect of the non-refundable tax offset there are three possible approaches for the accounting and presentation of the RD tax credit.
Treatment of tax in financial statements. Income tax treatment of foreign exchange gains or losses1. Assets whose tax basis is reduced by investment tax credits. May be treated in the customary deferred tax manner.
Please remember some aspects of your firms treatment of its tax. The change is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15 2018. The IFRIC noted that it would be appropriate in complying with IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements for entities to disclose whether they present their gross cash flows as inclusive or exclusive of VAT.
Just suppose that last year they estimated that the tax would be say 5000. Accounting Standards Update ASU 2018-02 allows business owners to reclassify the stranded tax effects of the TCJAs change in federal tax rates within accumulated other comprehensive income AOCI to retained earnings. Please remember some aspects of your firms treatment.
A tax computation is a statement showing the tax adjustments to the accounting profit to arrive at the income that is chargeable to tax. For example some fixed assets are tax deductible at once but can only be recognized through long-term depreciation in the financial statements. David Kindness is an accounting tax and finance expert.
These three core statements are. Notes to the Financial Statements For the financial year ended 31 December 2010 Notes to the Financial Statements 5. Tax adjustments include non-deductible expenses non-taxable receipts further deductions and capital allowances.
These accounts include payroll taxes wage garnishments and child support for example. The Committee published a tentative agenda decision. The entity should provide for the unavoidable tax.


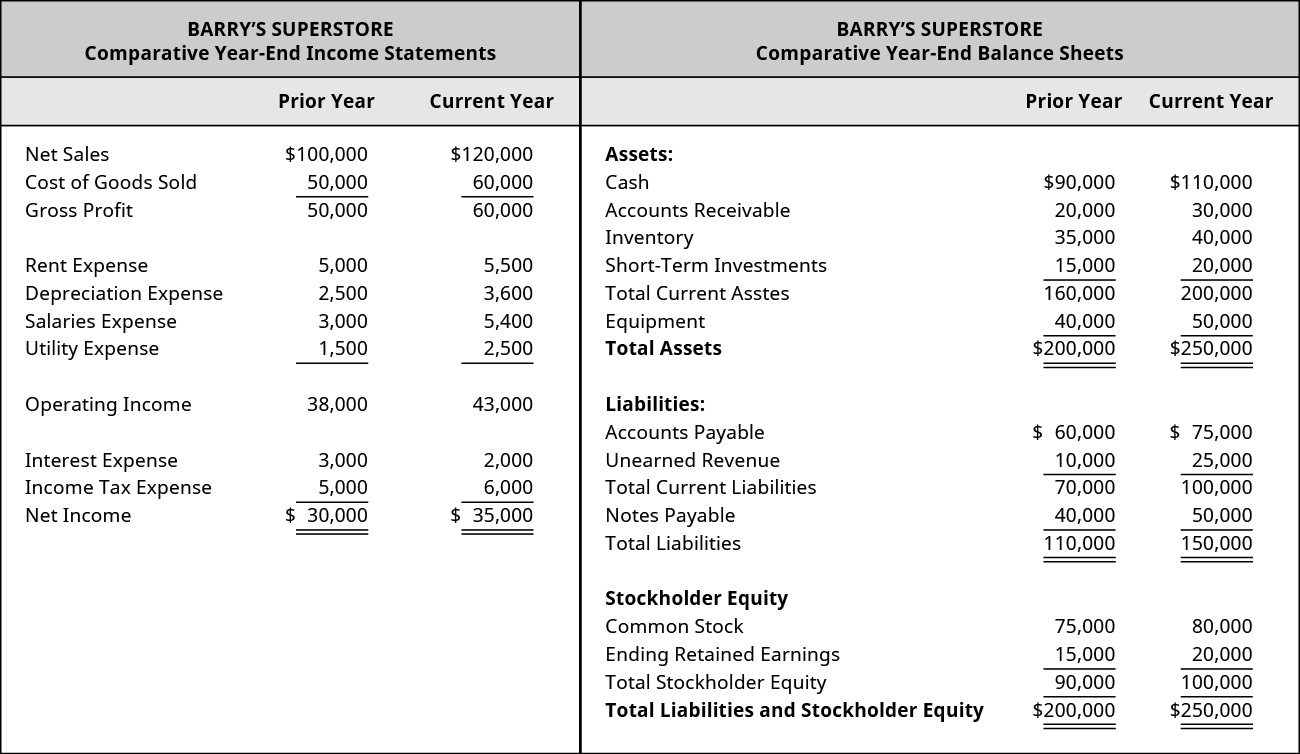
/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-01-3998c75d45bb4811ad235ef4eaf17593.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-02-6a82acc4cf2d4434a77899c09d49e737.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Financial_Statements_Aug_2020-01-3998c75d45bb4811ad235ef4eaf17593.jpg)